Central Emission Register of Buildings on the home straight!

A base called Central Building Emissions Register will be created. In a few months’ time, the owner or manager of the building will be submitting a written declaration to the head of the village council about the heat generating devices.
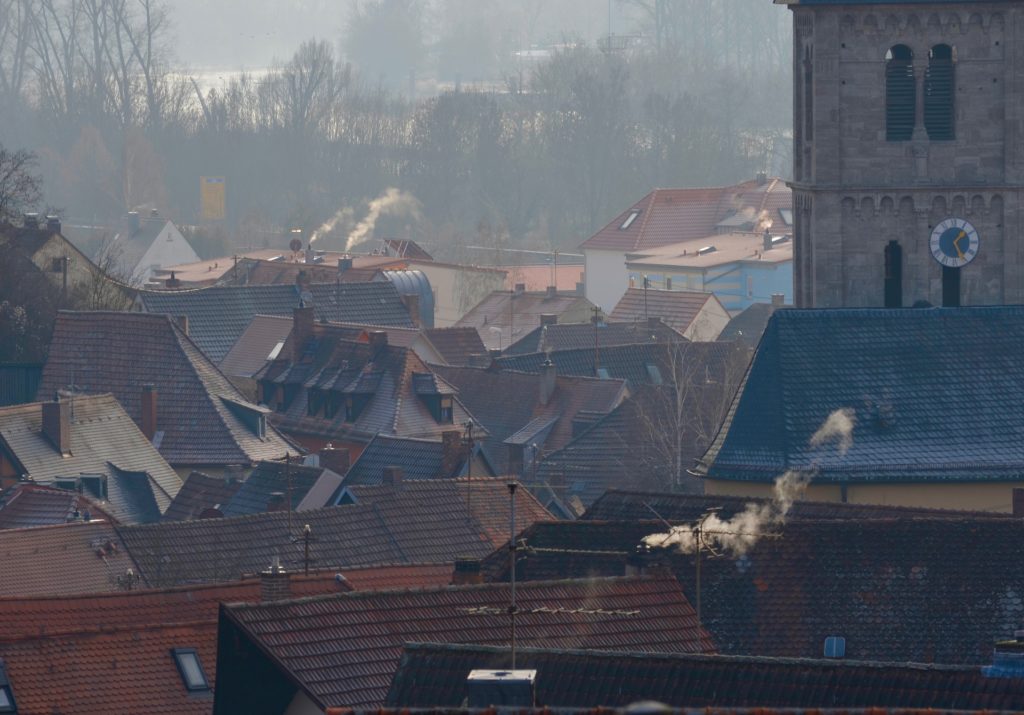
Fighting smog and energy poverty and improving the energy efficiency of buildings are the primary objectives of the emerging base. Ultimately, this measure is intended to eliminate dust emissions into the air from low-emissions, i.e. from the communal and living sector.
What is CEEB?
Central Building Emissions Inventory (CEEB) is an IT mechanism for identifying sources of low emissions from buildings. The system will collect key information on emission sources in the municipal and commercial sector.
The project assumes that the system will enable the collection of data on the energy condition of buildings. Information on forms of public aid (subsidies, preferential loans) granted for thermal upgrading or replacement of boilers in buildings.
The project assumes that the system will enable the collection of data on the energy condition of buildings. Information on forms of public aid (subsidies, preferential loans) granted for thermal upgrading or replacement of boilers in buildings.
The criterion for the entry of a building into the system will be the strength of the source, regardless of the legal form of use of the building. CEEB will therefore cover not only residential buildings but also public buildings, including small district heating plants or small production plants, provided that the rated thermal input of the fuel source used does not exceed 1 MW
– The government explains in an announcement
CEEB is intended to enable ongoing monitoring of information on available funding for air protection projects, including the thermal modernisation of a building or the replacement of old boilers with public funds.
The inventory is planned to cover around 5-6 million buildings, initially 500 000 buildings per year. The general building inventory will be combined with the submission of written declarations on heat and combustion sources – by the end of 2021.
Millions on fire
In Poland, over 80% of single-family buildings are heated with solid fuels. This includes 3 million using technologically outdated boilers for coal and wood, which emit significant amounts of pollutants. Over 70% of single-family houses do not have any thermal insulation or are poorly insulated. For years Poland has had the most polluted air in the entire European Union.
Małopolska inspires!
The Małopolska Region has launched the first building heating inventory database in Poland, which makes it possible to collect information on heating sources in a uniform manner at the voivodship level. The application enables free management of the building heating inventory and updating of data on heating exchanges, thermos modernizations and renewable energy sources used. The application makes it possible to monitor the implementation of the provisions of the Air Quality Plan and the progress of implementation of anti-smog resolutions. The database was made available at the beginning of 2017 to all 182 municipalities of the region. From the beginning of its operation until August 2020, approximately 260,000 Małopolska facilities have been entered into the database. The operation of the database was indicated as “good practice” during the control of the Supreme Audit Office conducted in 2018. The application is available at the following link: http://baza.powietrze.malopolska.pl. The obligation to prepare and update data in the inventory database results from the provisions of the Air Quality Plan for the Małopolska Region.
Currently, the inventory of heating sources in Małopolska, based on data entered in the database, is estimated at about 30%.
Representatives of the Małopolska Region took part in the works on the Central Building Emissions Inventory at the Ministry of Development.