Partnership is the key to success

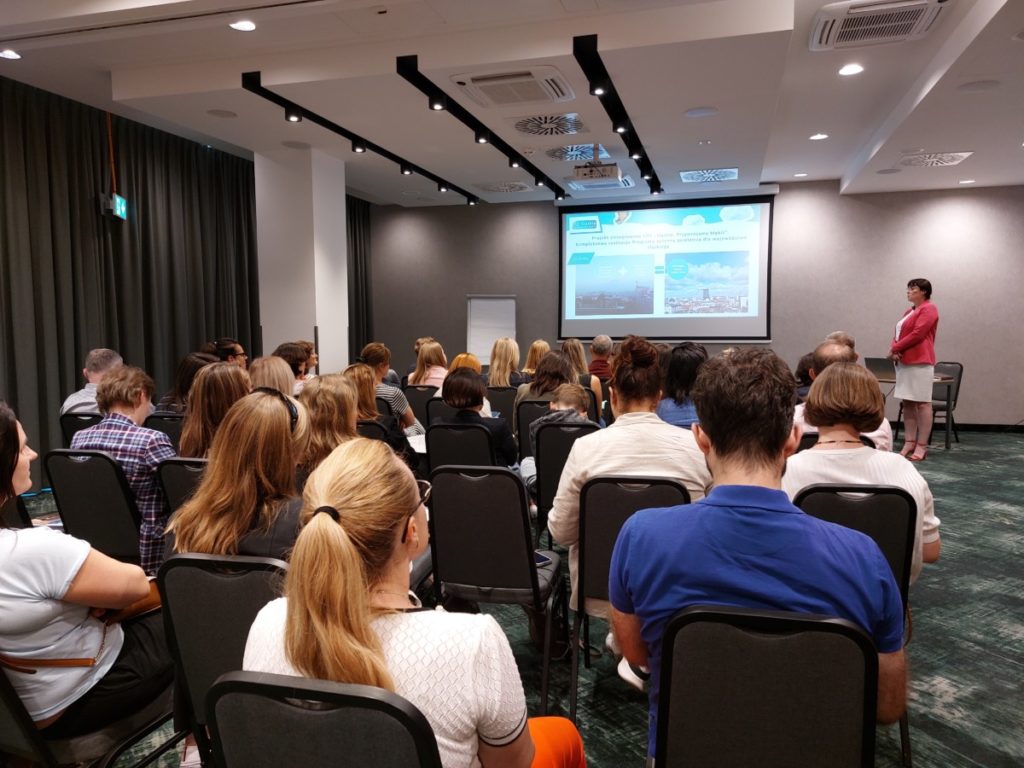
On 24-25 June 2024, Katowice became the centre of discussion on air protection thanks to a study visit by the Partnership: Environment for Development project. The meeting brought together air protection specialists from all over the country.
The Partnership: Environment for Development project, coordinated by the Ministry of Climate and Environment, aims to create a cooperation platform for organisations responsible for environmental protection and the exchange of knowledge and experience between those involved in the implementation of European funds. The event was attended by representatives of the Ministry, Marshal Offices, local administration and NGOs.
Sharing experience
The first day’s discussion focused on the preparation of Air Protection Programmes, the implementation of tasks and the reporting on their implementation. Good practices and mechanisms to support municipalities in the implementation of tasks included in the Programme were presented. Malopolska shared its experience in the implementation of the LIFE IP Malopolska project and the beginning of the project Implementation of the Air Protection Programme financed from the European Funds for Malopolska 2021-2027.
Science inspires action
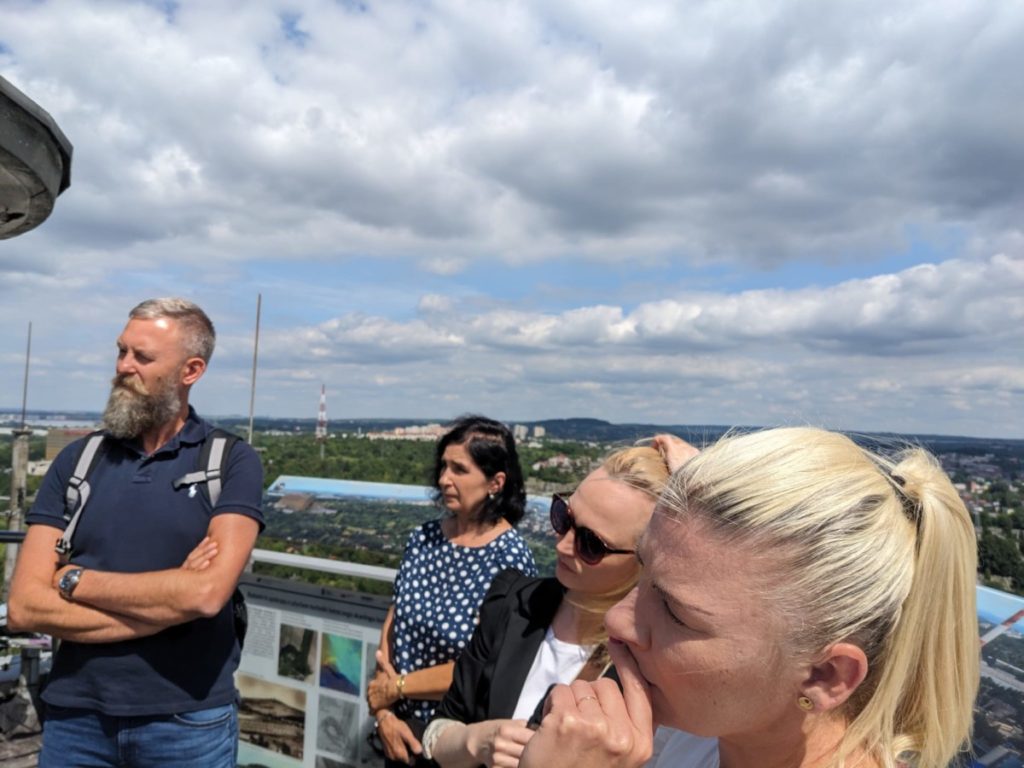
The second day of the visit included a trip to the University’s Atmospheric Control Laboratory in Sosnowiec. Researchers and students from the University of Silesia presented their innovative methods for studying atmospheric pollution.
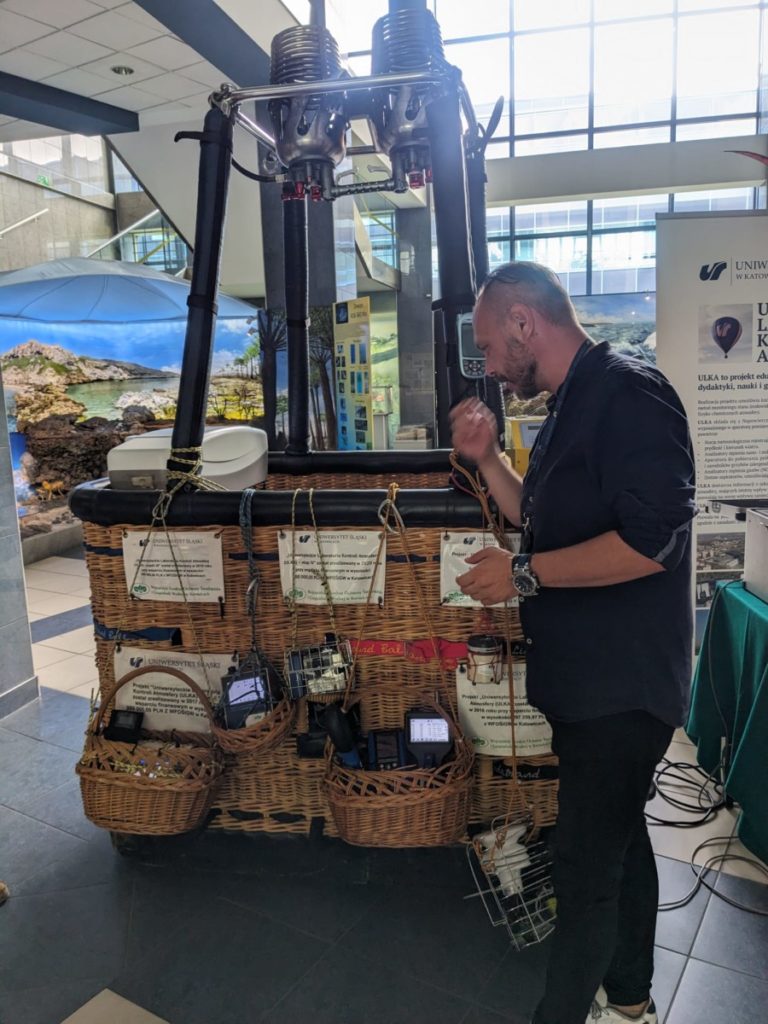
The laboratory uses three types of equipment:
- Flying laboratory – a hot air balloon with measuring apparatus.
- Mobile laboratory – an off-road vehicle with measuring equipment cooperating with the balloon.
- Stationary laboratories – research resources of the University of Silesia.
One of the most important pieces of equipment in the balloon is a nanoparticle analyser (from 10 to 300 nanometres). These tests are important in the context of the new Ambient Air Quality Directives (AAQD), which will make the monitoring of ultrafine particles in the air mandatory. Because smaller dust particles penetrate the body more easily and cause more serious damage, this research is crucial for planning preventive measures.